Overview
Benign prostate enlargement (BPE) affects men over 50 years old and is the term for an enlarged prostate. This impacts how a man urinates. It is not cancer and is not usually a serious threat to health.
Key Facts
- BPE is a condition that enlarges the prostate and affects how a man pees
- It is most common in men over 50
- Symptoms include difficulty in peeing, weak urine flow, frequent and urgent need to pee
- Lifestyle changes can help treat BPE
- Surgery can occur in cases where other treatments have not worked
Symptoms
Primarily, this affects how you pee so you may experience some of the following symptoms:
- Find it difficult to start peeing
- Having to strain to pee
- Experiencing a weak flow of urine
- “Stop-start” peeing
- Needing to pee urgently and/or frequently
- Needing to get up frequently in the night to pee
In most men, the symptoms are mild and do not need treatment. For others, they can be more severe.
It is worth noting that it can sometimes lead to such as:
- A urinary tract infection (UTI)
- Acute urinary retention, which is the sudden inability to pass any urine
Diagnosis
To find out if your prostate gland is enlarged, your doctor will conduct several tests.
The doctor will start by asking about your symptoms, any concerns you may have as well as the impact on your life. Additionally, the doctor is likely to do a physical exam including examining your stomach and genital area. It is also likely they will conduct a rectal exam to feel your prostate gland.
You may be asked to do blood and urine tests – the blood test to check your kidneys as well as a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test and the urine test to check for sugar (glucose) or blood in your pee.
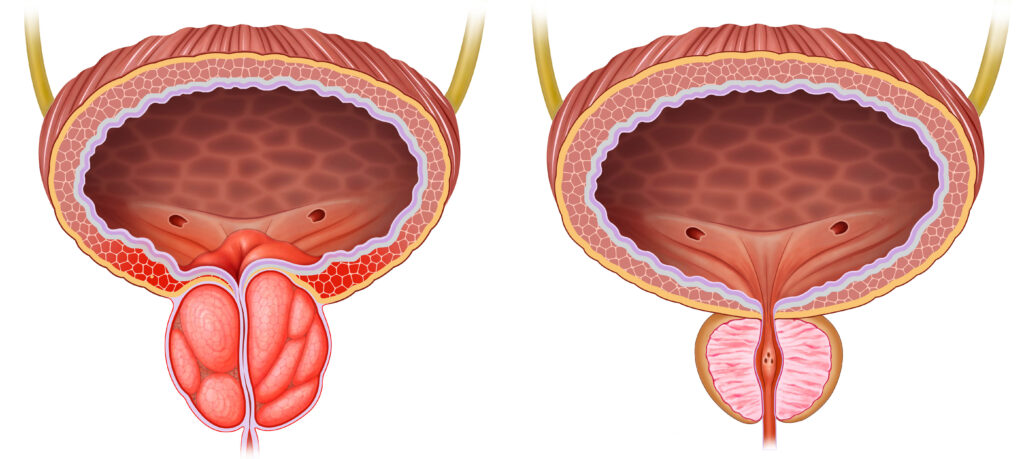
Causes
The prostate is a small gland in the pelvis about the size of a walnut, which is located in the pelvis, between the penis and bladder.
There is no exact cause of prostate enlargement, however it is believed that it is linked to changes in a man’s hormone levels as they get older.
Typical Treatments
Depending on the severity of the symptoms, your doctor will recommend different treatment options. If the symptoms are mild, it is unlikely that you’ll have any immediate treatment but rather have regular prostate check-ups as well as being advised to make lifestyle changes, such as:
- Drinking less alcohol, caffeine and fizzy drinks
- Limiting your intake of artificial sweeteners
- Exercising regularly
- Drinking less in the evening
If you are experiencing moderate or severe symptoms, you’ll be recommended medication that can reduce the size of the prostate and relax your bladder. These can include:
- Alpha-blockers which help relax the muscle in the prostate gland and at the base of your bladder, making it easier to pee
- Anticholinergics relaxes the bladder muscle if it is overactive
- 5-alpha reductase inhibitors help shrink the prostate gland if it is enlarged
- Diuretics can speed up urine production so that if they are taken during the day, it reduces the amount of urine produced overnight
- Desmopressin slows down urine production so less urine is produced during the night
If other treatments do not work, surgery may be recommended by your doctor. This can be:
- Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) which involves removing part of the prostate gland
- Open prostatectomy which removes the whole prostate gland if your prostate has enlarged over a certain size
Conclusion
Benign prostate enlargement is not normally a serious threat to a man’s health and can be managed by lifestyle changes and medication.
MOST COMMON
