Overview
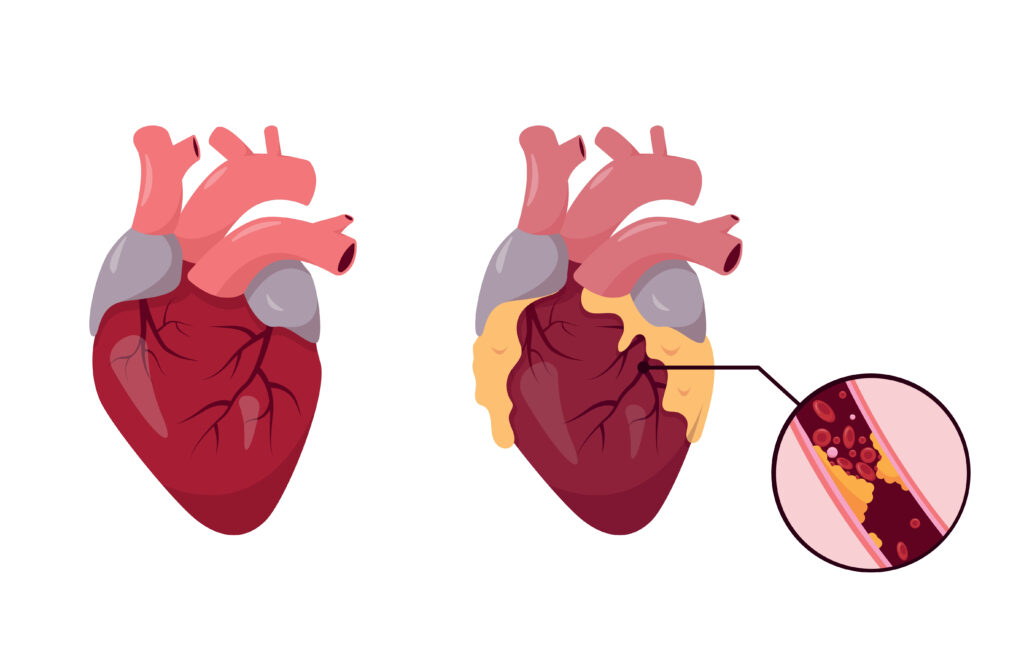
Coronary heart disease (sometimes known as ischemic heart disease or coronary artery disease) is a major cause of death worldwide. Coronary heart disease (CHD) develops when coronary arteries become too narrow. The condition causes blockages in the arteries that feed oxygen-rich blood to the heart.
It can not be cured but treatment helps manage the symptoms and reduces the chance of problems such as heart attacks. The risk of CHD can be reduced by making simple lifestyle changes.
Key Facts
- Coronary heart disease (CHD) is caused by an interruption of the heart’s blood supply through a build-up of fatty substances in the coronary arteries
- Lifestyle factors like smoking and excessive consumption of alcohol increase the risk of getting the disease
- Symptoms of heart attack can be similar to indigestion. These symptoms can include heaviness in the chest, stomach ache or heartburn
- Other health conditions like high blood pressure and diabetes can increase the risk of developing heart disease
- Regular exercise reduces the risk of a heart attack
Symptoms
The most common symptom is chest pain and is considered an early ‘warning sign’. This can be a mild, uncomfortable feeling similar to indigestion. However, more severe symptoms can cause a painful feeling of heaviness or tightness, usually in the centre of the chest, which then can spread to the arms, neck, jaw, back or stomach. Symptoms usually pass in less than 10 minutes,
Heart attacks
Unfortunately, for some people the first signs of CHD is a heart attack also called myocardial infarction.
During a heart attack, you may also have the following symptoms:
- pain starting in your chest and then spreading to other parts of the body – it can feel as if the pain is travelling from your chest to your arms, jaw, neck, back or stomach
- lightheadedness
- sweating
- nausea
- breathlessness
Heart Failure
When the heart becomes too weak to pump blood around the body, it can cause fluid to build up in the lungs, which makes it increasingly difficult to breathe.
Diagnosis
Your doctor can carry out a risk assessment for you which will start with getting a full medical and lifestyle history. It is important that you are honest with your doctor. They will also likely conduct some blood tests.
Depending on your answers and your risk factors, further tests may then occur including:
- A treadmill test
- A radionuclide scan
- A CT scan
- An MRI scan
- Coronary angiography
Causes
CHD is caused by a build-up of fatty deposits on the walls of the arteries around the heart. That fatty build-up narrows the arteries and restricts the flow of blood to the heart muscle. The risk is significantly increased if you:
- Smoke
- Have high blood pressure (hypertension)
- Have high cholesterol
- Have high levels of lipoprotein
- Do not exercise regularly
- Have diabetes
- Are obese or overweight
- Have a family history of CHD – the risk is increased if you have a male relative under the age of 55, or a female relative under 65, with CHD
Prevention
The key to prevention is living a healthy life by
- Eating a healthy, balanced diet –A low-fat, high-fibre diet is recommended, which should include plenty of fresh fruit and vegetables (5 portions a day) and whole grains.
- Being more physically active
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Giving up smoking
- Reducing your alcohol consumption
Typical Treatments
Depending on your own health circumstances and the severity of your CHD, your doctor will recommend treatment accordingly. This is normally done through lifestyle changes and/or medication to manage the symptoms and reduce the risk of other problems.
Medicines
There are different medications used to treat CHD, depending on your risk factors and symptoms. They normally aim to reduce blood pressure or widen your arteries. They can include:
- Blood thinners: these thin your blood and prevent it from clotting
- Statins: these block the formation of cholesterol and increase the number of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptors in the liver
- Beta blockers: are used to treat high blood pressure
- Nitrates: these are used to widen your blood vessels
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors: these are used to treat high blood pressure
- Calcium channel blockers: these decrease your blood pressure by relaxing the muscles that make up the walls of the arteries
Surgery
If the arteries to your heart are narrow due to the build-up of fatty deposits or your symptoms can not be controlled using medicinee, your doctor may recommend surgery. These can include:
- Coronary angioplasty
- Coronary artery bypass graft
- Heart transplant
Conclusion
The key to prevention is a healthy lifestyle combined of having a balanced diet and regular exercise. People should seek immediate medical help if they have chest pain and breathlessness, as this could indicate a heart attack.
MOST COMMON